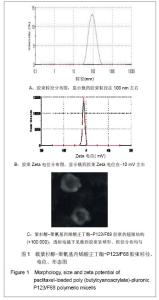
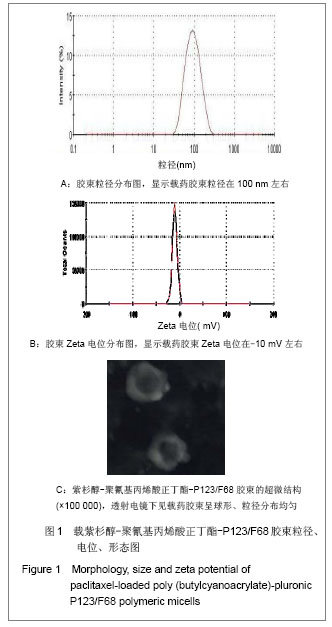
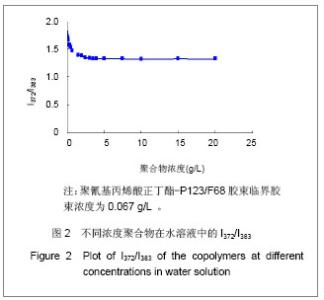
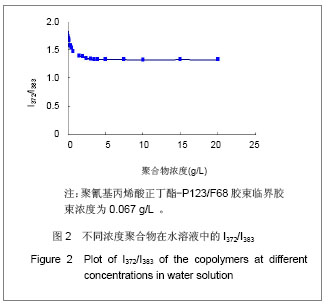
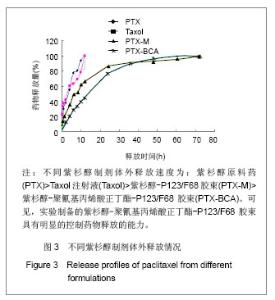
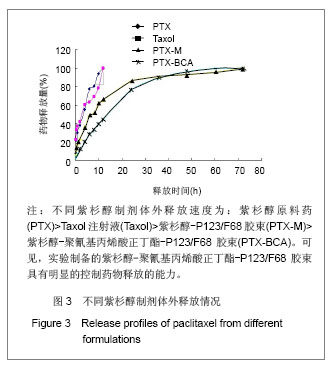
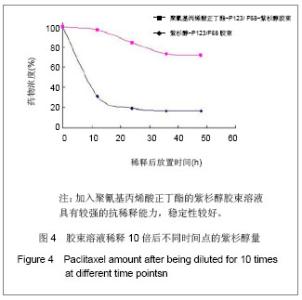
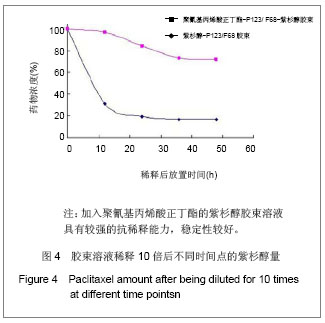
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (16): 2935-2942.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.16.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
Controlled drug release capability of paclitaxel-loaded poly(butylcyanoacrylate)-pluronic P123/F68 polymeric micells
Zhang Yang-de1, Xu Hong-juan1, Liang Jian2, Wang Ji-wei1, Pan Yi-feng1, Deng Xin2
- 1 National Hepatobiliary and Enteric Surgery Research Center, Ministry of Health, Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China
2 Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2013-01-19Revised:2013-03-15Online:2013-04-16Published:2013-04-16 -
Contact:Liang Jian, Doctor, Professor, Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhang Yang-de☆, Doctor, Professor, National Hepatobiliary and Enteric Surgery Research Center, Ministry of Health, Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China 530222867@qq.com -
Supported by:the International S&T Cooperation Program of China, No. 2011DFA32620*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Yang-de, Xu Hong-juan, Liang Jian, Wang Ji-wei, Pan Yi-feng, Deng Xin. Controlled drug release capability of paclitaxel-loaded poly(butylcyanoacrylate)-pluronic P123/F68 polymeric micells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(16): 2935-2942.
share this article
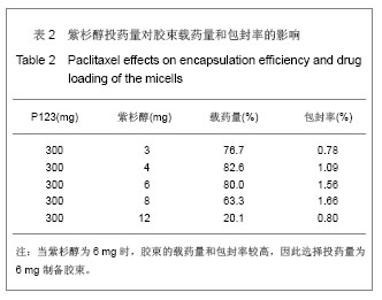
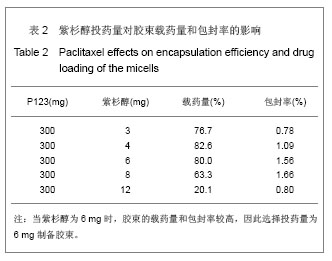
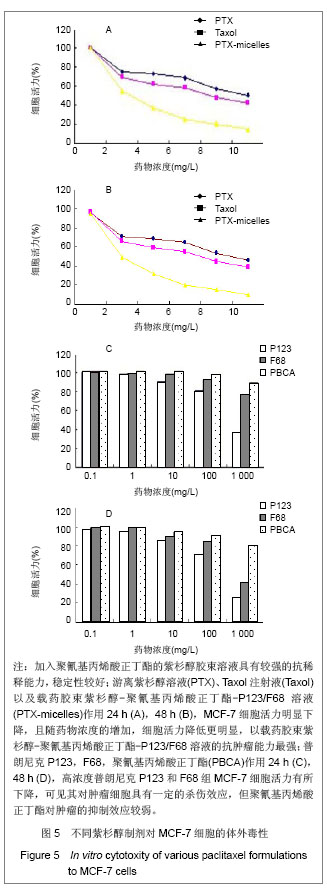
2.6 载药胶束的细胞毒性 体外抗癌活性的研究是确定抗肿瘤药物药效的方法之一。抗肿瘤药物的抗癌活性可用半数抑制浓度(IC50)进行定量表示,IC50是指在用药后存活的细胞数量减少一半所需的药物浓度[5] 。采用MTT方法,探测紫杉醇-聚氰基丙烯酸正丁酯- P123/F68对MCF-7的IC50,并与紫杉醇原料药和Taxol注射液进行比较,见图5。 由图5可见,当药物与细胞作用24 h时,紫杉醇原料药、Taxol注射液、载药胶束的IC50分别是13.47,7.59,2.38 mg/L;而当作用时间为48 h时,三者的IC50分别变为10.64,6.25,2.03 mg/L。因此,在两个时间点,与游离药物和注射液相比,载药胶束均显示较强的杀死肿瘤细胞的能力。同时,普朗尼克P123和F68在一定的作用时间和浓度下,对肿瘤细胞同样具有一定的杀伤效应,这与文献记载是一致的,但是聚氰基丙烯酸正丁酯对肿瘤的抑制效应较弱,具有良好的生物相容性。"
| [1]Marupudi NI, Han JE, Li KW, et al. Paclitaxel: a review of adverse toxicities and novel delivery strategies. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2007;6(5):609-621.[2]Gogate US, Schwartz PA, Agharkar SN. Effect of unpurfied Cremophor EL on the solution stability of paclitaxel. Pharm Dev Technol. 2009;14(1):1-8.[3]Huh KM, Min HS, Lee SC, et al. A new hydrotropic block copolymer micelle system for aqueous solubilization of paclitaxel. J Control Release. 2008;126(2):122-129.[4]Yang T, Choi MK, Cui FD, et al. Preparation and evaluation of paclitaxel-loaded PEGylated immunoliposome. J Control Release. 2007;120(3):169-177.[5]Wei Z, Hao J, Yuan S, et al. Paclitaxel-loaded Pluronic P123/F127 mixed polymeric micelles: formulation, optimization and in vitro characterization. Int J Pharm. 2009;376(1-2):176-185.[6]Dahmani FZ, Yang H, Zhou J, et al. Enhanced oral bioavailability of paclitaxel in pluronic/LHR mixed polymeric micelles: preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2012;47(1):179-189.[7]Oh KS, Song JY, Cho SH, et al. Paclitaxel-loaded Pluronic nanoparticles formed by a temperature-induced phase transition for cancer therapy. J Control Release. 2010; 148(3): 344-350.[8]Liu J, Meisner D, Kwong E, et al. A novel trans-lymphatic drug delivery system: implantable gelatin sponge impregnated with PLGA-paclitaxel microspheres. Biomaterials. 2007;28(21): 3236-3244.[9]Parka IlK, Kimb YJ, Trana TH, et al. Water-soluble heparin-PTX conjugates for cancer targeting. Polymer. 2010; 51(15):3387-3393.[10]Ooya T, Lee J, Park K. Effects of ethylene glycol-based graft, star-shaped, and dendritic polymers on solubilization and controlled release of paclitaxel. J Control Release. 2003;93(2): 121-127.[11]Kedar U, Phutane P, Shidhaye S, et al. Advances in polymeric micelles for drug delivery and tumor targeting. Nanomedicine. 2010;6(6):714-729.[12]Batrakova EV, Li S, Brynskikh AM, et al. Effects of pluronic and doxorubicin on drug uptake, cellular metabolism, apoptosis and tumor inhibition in animal models of MDR cancers. J Control Release. 2010;143(3):290-301.[13]Han LM, Guo J, Zhang LJ, et al. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of polymeric micelles of paclitaxel with Pluronic P123. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2006;27(6):747-753.[14]Jansson J, Schillén K, Olofsson G, et al. The interaction between PEO-PPO-PEO triblock copolymers and ionic surfactants in aqueous solution studied using light scattering and calorimetry. J Phys Chem B. 2004;108(1):82-92.[15]Wulff-Pérez M, Torcello-Gómez A, Gálvez-Ruíz MJ, et al. Stability of emulsions for parenteral feeding: preparation and characterization of o/w nanoemulsions with natural oils and Pluronic f68 as surfactant. Food Hydrocolloids. 2009;23(4): 1096-1102.[16]Cha MH, Choi J, Choi BG, et al. Synthesis and characterization of novel thermo-responsive F68 block copolymers with cell-adhesive RGD peptide. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2011;360(1):78-85. [17]Dabholkar RD, Sawant RM, Mongayt DA, et al. Polyethylene glycol-phosphatidylethanolamine conjugate (PEG-PE)-based mixed micelles: some properties, loading with paclitaxel, and modulation of P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux. Int J Pharm. 2006;315(1-2):148-157.[18]Zhao L, Du J, Duan Y, et al. Curcumin loaded mixed micelles composed of Pluronic P123 and F68: preparation, optimization and in vitro characterization. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2012;97:101-108.[19]Wang L, Zeng R, Li C, et al. Self-assembled polypeptide- block-poly(vinylpyrrolidone) as prospective drug-delivery systems. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2009;74(1):284-292.[20]Adams ML, Lavasanifar A, Kwon GS. Amphiphilic block copolymers for drug delivery. J Pharm Sci. 2003;92(7): 1343-1355.[21]Lin J, Zhu J, Chen T, et al. Drug releasing behavior of hybrid micelles containing polypeptide triblock copolymer. Biomaterials. 2009;30(1):108-117.[22]Van Butsele K, Sibret P, Fustin CA, et al. Synthesis and pH-dependent micellization of diblock copolymer mixtures. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2009;329(2):235-243.[23]Zhang J, Jiang W, Zhao X, et al. Preparation and characterization of polymeric micelles from poly (D,L-lactide) and methoxypolyethylene glycol block copolymers as potential drug carriers. Tsinghua Sci Technol. 2007;12(4):493-496.[24]Taillefer J, Jones MC, Brasseur N, et al. Preparation and characterization of pH-responsive polymeric micelles for the delivery of photosensitizing anticancer drugs. J Pharm Sci. 2000;89(1):52-62.[25]Sezgin Z, Yüksel N, Baykara T. Preparation and characterization of polymeric micelles for solubilization of poorly soluble anticancer drugs. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2006;64(3):261-268.[26]Liao DL, WU GS, Liao BQ. Zeta potential of shape-controlled TiO2 nanoparticles with surfactants. Colloids and surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects. 2009;348(1-3): 270-275.[27]Liu Y, Cao X, Luo M, et al. Self-assembled micellar nanoparticles of a novel star copolymer for thermo and pH dual-responsive drug release. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2009; 329(2):244-252.[28]Wang XH. Changsha: Central South University. 2007.王夏红.苯妥英钠聚氰基丙烯酸正丁酯纳米微粒的制备及抗癫痫的药效学研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2007.[29]Agnihotri SA, Mallikarjuna NN, Aminabhavi TM. Recent advances on chitosan-based micro- and nanoparticles in drug delivery. J Control Release. 2004;100(1):5-28. |
| [1] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Gu Xia, Zhao Min, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Relationship between hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and hypoxia signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [6] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [7] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [8] | He Jie, Chang Qi. Biological reconstruction of large bone defects after resection of malignant tumor of extremities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 420-425. |
| [9] | Yu Langbo, Qing Mingsong, Zhao Chuntao, Peng Jiachen. Hot issues in clinical application of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in orthopedics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 449-455. |
| [10] | Li Xinping, Cui Qiuju, Zeng Shuguang, Ran Gaoying, Zhang Zhaoqiang, Liu Xianwen, Fang Wei, Xu Shuaimei. Effect of modification of β-tricalcium phosphate/chitosan hydrogel on growth and mineralization of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3493-3499. |
| [11] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| [12] | He Lin, Wu Xi, He Song, Yang Sen. Hydrophilicity and cell adhesion of hydroxyapatite bioceramics after the coating of polydopamine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3540-3544. |
| [13] | Zhou Anqi, Tang Yufei, Wu Bingfeng, Xiang Lin. Designing of periosteum tissue engineering: combination of generality and individuality [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| [14] | Lang Limin, He Sheng, Jiang Zengyu, Hu Yiyi, Zhang Zhixing, Liang Minqian. Application progress of conductive composite materials in the field of tissue engineering treatment of myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590. |
| [15] | Ma Qing, Shi Liyan, Huang Sixue, Zheng Zhangbowen, Zhang Aihua, Zhan Desong, Fu Jiale. Research status and prospect of zirconia ceramics in dental prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3597-3602. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||